07 Jan 2026
By : dolly / Comments 0
Creating Dynamic Blocks in AutoCAD: A Practical Guide for Drafters
In architectural and engineering drafting, efficiency and consistency are critical. Repetitive elements such as doors, windows, furniture, electrical symbols and fixtures can significantly slow down the drafting if recreated every time. This is where the Dynamic Blocks in AutoCAD becomes a powerful productivity tool—allowing a single block to adapt to multiple conditions without creating the separate block files.
This blog walks you through what the dynamic blocks are, why they matter and how to create them step by step for reusable components.
What Are Dynamic Blocks in AutoCAD?
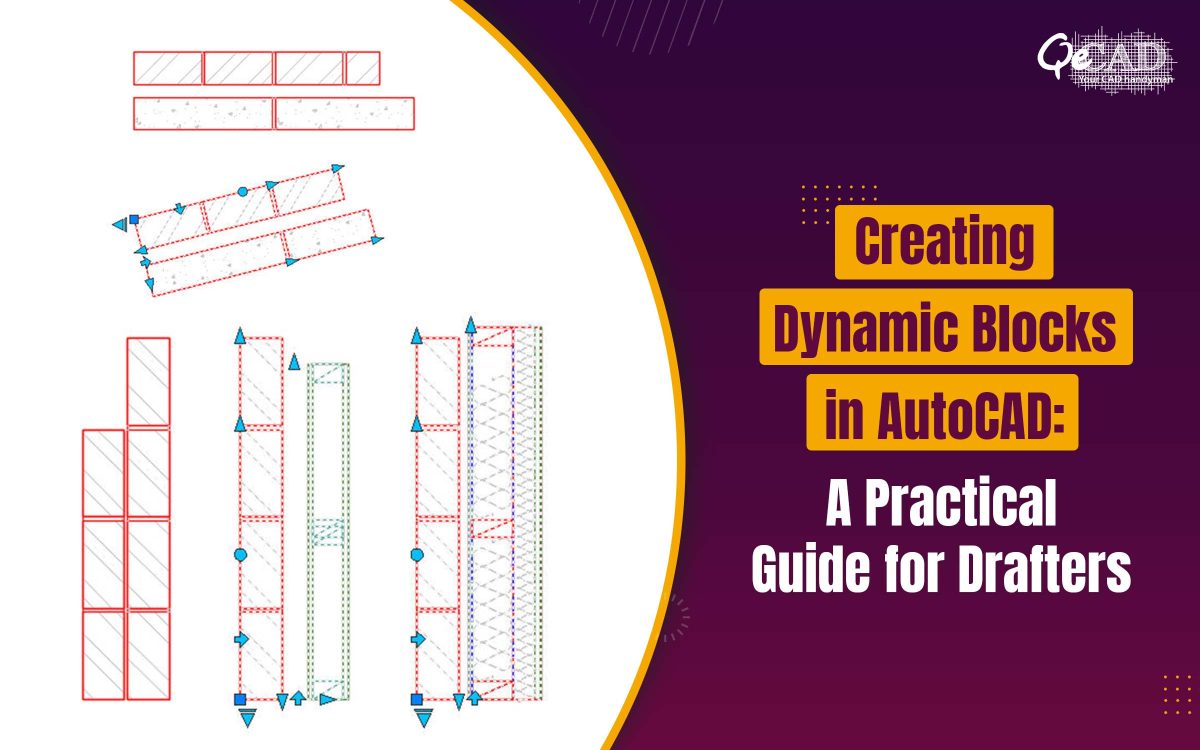
Dynamic blocks are enhanced AutoCAD blocks that contains the parameters and actions enabling them to change the shape, size or appearance. Instead of inserting multiple static blocks, you can insert one intelligent block and modify it directly in the drawing.
For example:
- A single door block can represent the different widths and swing directions
- A window block can adjust its size without redrawing
- Furniture blocks can stretch to fit various layouts
Why Use Dynamic Blocks?
Using dynamic blocks offers several advantages:
- Reduces file clutter by replacing multiple block variations
- Improves drafting speed and reduces the repetitive work
- Maintains consistency across the drawings
- Simplifies revisions when design changes occur
- Improves accuracy in architectural and construction documentation
Dynamic blocks are especially valuable in the architectural and engineering drawings where the standard components are reused across the projects.
A Practical Guide to Building Dynamic Blocks in AutoCAD
Step 1: Create the Base Geometry
Start by drafting the object that will become your block—for example, a door, window or the furniture layout. Ensure that the geometry is clean, properly layered and drawn at the correct scale.
Step 2: Convert the Object into a Block
- Select the geometry
- Type BLOCK or B in the command line
- Define a block name and insertion point
- Click OK
This creates a standard block that will now be enhanced with the dynamic features.
Step 3: Open the Block Editor
- Select the block
- Right-click and choose Block Editor, or type BEDIT
The Block Editor environment allows you to add intelligence to the block using parameters and actions.
Step 4: Add Parameters
Parameters defines what can change in the block. Common parameters includes:
- Linear – Controls length or width
- Rotation – Allows rotation (e.g., door swing)
- Flip – Creates mirrored versions
- Visibility – Switches between different components or styles
Choose a parameter from the Parameters tab in the Block Authoring Palette and place it appropriately on the block.
Step 5: Assign Actions to Parameters
Actions define how the geometry responds to the parameter changes. Common actions includes:
- Stretch – Resizes geometry
- Move – Shifts elements
- Rotate – Rotates objects
- Flip – Mirrors geometry
- Visibility – Shows or hides objects
Each parameter must be linked to an action. Select the geometry carefully to ensure only the intended elements are affected.
Step 6: Test the Dynamic Block
Use the Test Block option in the Block Editor to verify the functionality. Adjust grip points, test different sizes or orientations and confirm smooth behavior.
If something doesn’t behave as expected, return to the editor and refine parameter-action relationships.
Step 7: Save and Use the Block
Once testing is complete:
- Save the block
- Insert it into your drawing using INSERT
- Modify the block dynamically using grip points, without the need to explode or redefine it.
Your reusable component is now ready for production use.
Smart Practices for Developing Reusable Dynamic Blocks
- Keep dynamic blocks simple and focused
- Avoid overloading a single block with too many parameters
- Use clear naming conventions for parameters
- Test blocks in real project drawings
- Store frequently used dynamic blocks in a shared library
These practices ensure the long-term usability and consistency across teams.
Where Dynamic Blocks Fit into Professional Workflows
Dynamic blocks are commonly used in the architectural plans, MEP layouts, interior fit-outs and construction documentation. When combined with the professional workflows such as CAD Conversion Services, dynamic blocks helps in standardizing the legacy drawings and improves the drafting efficiency across projects. Similarly, they play a vital role in delivering accurate and consistent outputs in Architectural Drafting Services, especially for the large-scale or multi-phase developments.
Conclusion
Dynamic blocks transforms AutoCAD from a basic drafting tool into a powerful, intelligent design platform. By investing time in creating reusable dynamic components, teams can dramatically improve the efficiency, accuracy and consistency across drawings.
Whether you’re working on the architectural layouts, construction documents or renovation plans, mastering the dynamic blocks is a practical skill that pays off in every project.